
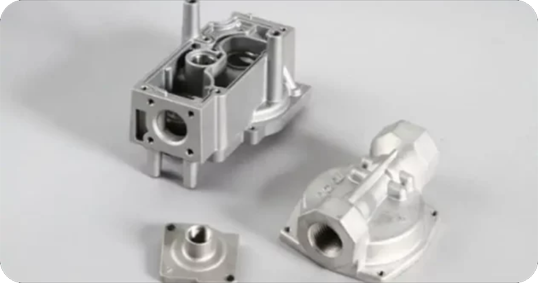
Die casting is a significant process for applications in various industries. An essential component of the die casting process is the die casting mold. The shape and characteristics of the mold affect the features of the final product.
Therefore, there is a need to understand the die casting mold design. This will help you design and choose the right mold for your die casting projects. Furthermore, you can be sure that the final product will meet unique manufacturing requirements.
Thus, this article will give you a detailed overview of the different types of die cast tooling. You would also learn how to design a mold and the factors you need to consider when making die casting tooling.
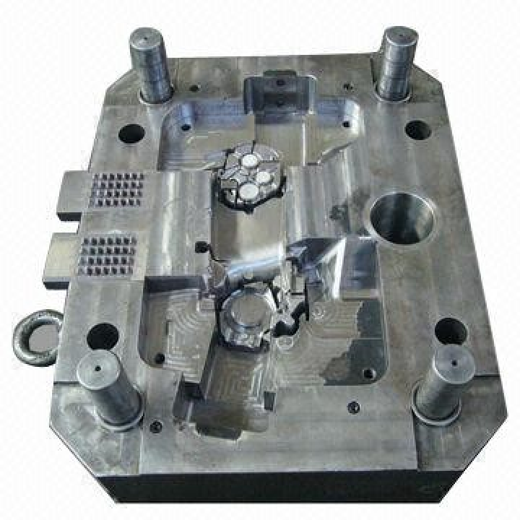

Wrong specifications can result in material or tool corrosion. Nevertheless, a proper mold design can boost the product’s time and efficiency. Ultimately, the quality of mold structure will determine whether production would proceed smoothly and castings would be of the best quality.
Moreover, the die cast tool design essentially reflects the different factors that may occur during production. Thus, you must analyze a casting’s structure during design. It is also essential to master filing conditions, implement critical process parameters, and consider other economic effects. This will ensure that die casting tools can meet essential production requirements.
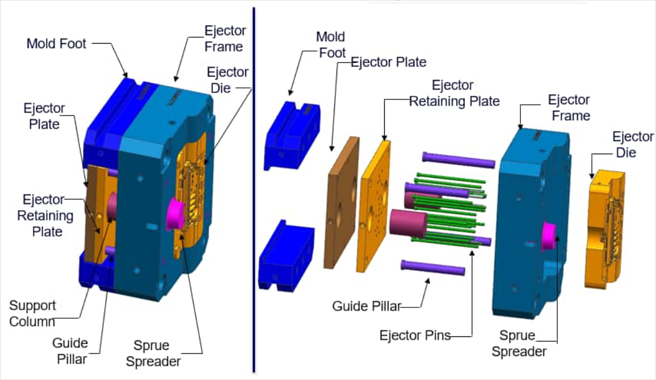
· Molding System
This includes the cavity, core, inserts, sliders, and insert pins. The die casting cavity determines the casting shape as the moving core closes.
· Mold Base System
The primary components of the die cast mould base system are steel plates and frames. This system combines different parts of the mold and allows mold installation on the die casting machine.
· Ejection System
This system works to eject parts from the mold. These parts include ejection, returned, and guiding parts.
· Runner System
The runner system connects with the die casting part and pressure chamber. Thus, it guides the metal material into the die cavity in a specific direction. This system directly impacts the pressure and speed of molten metal. The runner system components are a runner, a sprue, an inner gate, etc.
· Overflow System
This channel removes air from the pressure chamber. Generally, the primary components are overflow slots and venting slots. However, manufacturers install vent plugs in the deep cavities to improve venting conditions.
· Others
Other die casting mold components include positioning parts for placing parts correctly in the mold. In addition, there are pins and bolts for fastening purposes.
A significant investment in die casting is a fully-featured custom-made die. Therefore, a prototype die helps to make quite a number of casts to test for the different parts. The prototyping strategies are gravity casting, machined hog outs, and 3D printed parts. However, they involve trade-offs on properties, tolerance, and design.

A high-pressure die casting prototype will be your best option whenever you need the same alloy, properties, process, and geometry in place for production. Prototyping dies can utilize pre-hardened, uncoated tool steels and standardized components. As a result, they can be produced in short times and at a reduced cost.
Unlike other production techniques, these molds also make use of less efficient ejection or cooling techniques. Therefore, you must note that the tool won’t last for long, and the die won’t be as efficient as a production. However, this will not be an issue if you only need a small amount of casting.
Rapid Tooling Dies
Rapid tooling refers to inserts and dies produced using methods with shorter lead times than conventional methods. As opposed to rough machining and heat treating, the rapid tooling methods are selective laser sintering, direct metal deposition, laser engineered net shaping, etc.
Therefore, you’d expect the creation of these die cast tooling dies to be much faster. Manufacturers may use these dies either as prototyping dies or as production dies. The most viable choice will depend on the production volume requirements.
Production Dies
These dies are the most common types of die casting dies. Production dies are essential when all the design has been finalized and is ready for launching into an authentic product.

|
We can have:
The cavity material is high-quality steel, and it is often retained in a holder block. The design of production dies ensures that they have critical dimensions. Thus, you can be sure that they allow the required machining specifications. |
Unit Dies
The unit die is a special type of die casting mould. A die caster unit holder keeps the unit dies or customer-owned cavity within the cavity intact. We can have either single or double unitholders. Typical examples of sizes of cavity blocks that the dies hold are 8 x 10, 10 x 12, 12 x 15, and 15 x 18 (all in inches).
The unit dies employ generic pieces used for less complex components with a low volume. A custom die is more effective for higher volume parts with complex geometry. These dies are specifically designed for a part, providing maximum control and efficiency.
Preliminary Phase
Before designing the mold, it is important to check the part’s manufacturability with die casting technology. This phase involves judging the practicability of the product from a geometrical and dimensional.
Dimensional View: There is a need to know the dimension of the part and the number of cavities required for each casting. This will help know the opening force and the volume of the casting. The knowledge of this data will make feasibility studies a lot easier.
Geometrical View: The geometry of the parts includes drawing the parting line. The parting line divides the die casting mold into two, allowing easy mold opening and ejection of casting. Furthermore, the surface of parts depends on their position from parting lines. Consequently, surfaces have to be designed in the direction of mold opening.

The geometric tolerance of quotes found on the 2D model can be pretty hard to produce due to the shrinkage caused by metal cooling. The higher the number of quotes, the more difficult it is to get the same value on the casting. Therefore, you can go ahead with the die cast mold design as soon as you confirm the part’s manufacturability.
Number of Cavities
To know the number of cavities, you must consider the number of pieces to produce, cavity orientation, and the hypothetical cycle time. This way, you can decide the best option between a multi-cavity or a single-cavity mold.
When going for a multi-cavity mold, remember that aside from the fact that ejection phases and complexity of filling increase, the production process might be affected by the cavity’s dimension and product disposition.
Projection Area
The projection area is the surface gotten from the projection of cavities on the plan. It is perpendicular to the direction of the mold opening. The projection area is a vital component of the design phase. It relates the opening force from the molten metal to the die walls. As a result, the strength of the force will depend on the shape dimension orientation. A strong force will cause an overflow of material, thereby resulting in the formation of burrs.
Therefore you need to estimate the forces produced by the molten metal to prevent this casting defect. The force is the product of specific machine pressure, projection area, and pre-set safety factors. The factor offers a wider margin to help counter the maximum pressure after filling. Many people refer to it as a water hammer.
The machine transfers the dynamic and static force at the end of the process. Thus, there is the production of a pressure pick that the closing machine force must absorb. This closing force depends on the stroke dimension and press model.
Volume and Shape of the Die
The volume and shape of the die are essential for mold design. In addition to the volume desired, consider that the large parts will shrink due to a longer cooling time, increasing the shrinkage rate. Therefore, there is the need to size the mold cavities accordingly.
Unit Dies
The unit die is a special type of die casting mould. A die caster unit holder keeps the unit dies or customer-owned cavity within the cavity intact. We can have either single or double unitholders. Typical examples of sizes of cavity blocks that the dies hold are 8 x 10, 10 x 12, 12 x 15, and 15 x 18 (all in inches).
The unit dies employ generic pieces used for less complex components with a low volume. A custom die is more effective for higher volume parts with complex geometry. These dies are specifically designed for a part, providing maximum control and efficiency.

Before making die cast tooling, there are some things to look out for to guide in die cast tool design. They include:
Understanding die casting mold design will make your die casting project easier. It will also help you save some time and money. However, you need the service of experts to get the right tool for the best results. Hyer Mold offers the best precision die casting services for custom metal parts, providing quality tools, experts, and easy processes.
We have a wide range of materials, manufacturing processes, and surface finishing options for your die casting parts. Also, our experts offer you manufacturing suggestions to ensure you get the most effective solution. After placing the order for die casting parts, Hyer Mold manufacturing partners would produce perfect die casting tooling to make the best die-casted parts. Upload your design file today and get an instant quote.

